Mankind has always had a deep fascination and integral relationship with our sun. It has been the main source of fuel for our natural world for billions of years and will continue to burn bright long into the future. Since we began manipulating the earth beneath us, our technological advancements have propelled us to create incredible innovations. Solar panel technology might seem like a product of the modern era but its history goes back thousands of years. Its creative process began during ancient times and since then it has undergone an evolution that has progressed into the marvel that we reap the benefits of today. Let’s take a look at a brief history of solar energy
Timeline
Ancient Eras
From Ra to Helios, the ancient world worshiped the sun and understood its immense importance. The success of agrarian society depended on the timing and power of the sun’s rays. Intellectuals of the time observed this power and knew that there was a way to harness it and use it in incredibly innovative ways.

- 3rd Century B.C – Greeks and Romans use “Burning Mirrors” to light torches at religious ceremonies, thus becoming the oldest known use of solar energy in recorded history.
Modern Era
From the times of the ancients to the time of the modern era, constant war and the black plague put a halt to technological advancements. Besides the European renaissance of the 16th century, the industrial revolution of the 1800s became the period that brought about the most progression in technologies. Solar panels were no exception and the industrial revolution saw the birth of modern solar panels. Once the initial inventions were patented, the floodgates opened and gave way to the rapid transformation of efficient solar systems.
- 1839 – French Physicist, Edmond Becquerel first observes and discovers the photovoltaic effect, a chemical phenomenon that generates an electrical current when exposed to light. He did this at the young age of 19 by using silver bromide to coat platinum electrodes. Once they were illuminated by the sun, they generated energy.

- 1860’s – Augustin Mouchat becomes the first pioneer of solar energy. During his studies, he invented the first steam engine heated by solar rays. He did this because he believed that the coal used to power the industrial revolution would eventually run out.
- 1883 – Charles Fritts, an inventor from New York creates the first photovoltaic solar cell, putting out a meager but respectable 1-2% energy conversion rate. His selenium-based cell was attached to a rooftop in New York.
- 1888 – The first solar devices were patented by Edward Weston. In his words his device would “transform radiant energy derived from the sun into electrical energy, or through electrical energy into mechanical energy.”
World War I & II
The horrible nature of two global conflicts shook the world to its core. Nations around the world poured all of their efforts into the war effort. While this would result in a gap in the advancement of solar, it drove scientists and inventors to push the boundaries of their work and would eventually lay the grounds for the Cold War and the Space Race. This was a pivotal era in the history of solar energy.
- 1939 – Russell Ohl invents the solar design still used today in many modern panels. He would go on to make great strides in the area of semiconductors and eventually invent the transistor.
- 1948 – Eleanor Raymond designs and constructs the world’s first modern residence heated solely by solar energy. The house was built in Dover, Massachusetts.

- 1954 – Bell Laboratories creates the first silicon solar cell, converting away from selenium-based solar technologies. Its inventor was a man named Daryl Chapin.
Solar in Space
Simply put, it would have been impossible for mankind to achieve what it has in regard to space exploration without the power of solar panels. The use of solar panel technology was a pivotal factor in powering our satellites in spacecraft and continues to power all of the satellites, space telescopes and space stations currently in earth’s orbit.
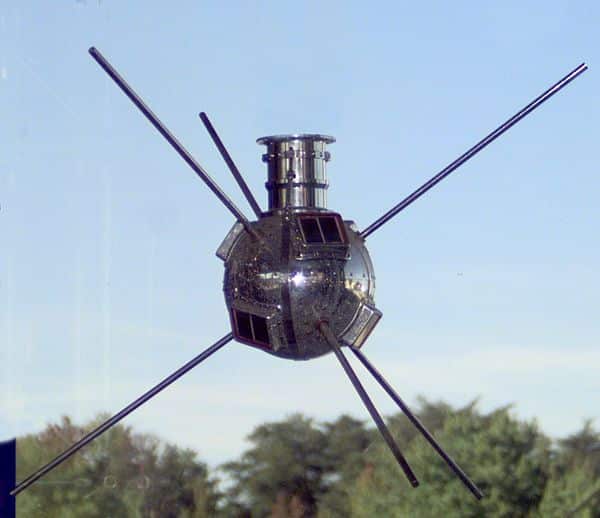
- 1958 – United States Navy launches Vanguard 1 in response to Russia’s Sputnik satellite. Contrary to Sputnik, which used battery packs and lasted for 21 days, the Vanguard utilized single-watt solar panels and is still transmitting today.

- 1960 – Hoffman Electronics raises solar efficiency from 8% to 14%. Mainly working on solar for satellites in the 1950s, company president H. Leslie Hoffman believed that solar technology could be used to power other common products. The company would manufacture an early solar-powered radio for public use.
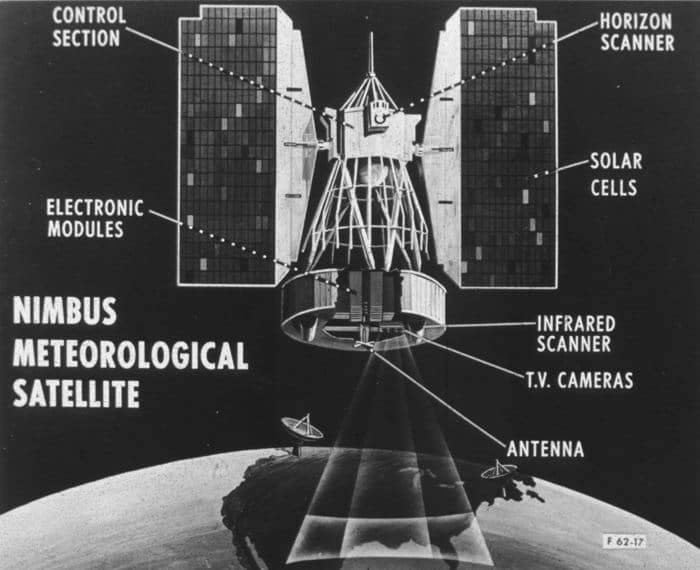
- 1964 – Newly formed NASA launches the first Nimbus spacecraft satellite, powered entirely by a 470-watt solar array. A total of seven Nimbus satellites were launched for meteorological research and data collection, all powered by solar panels.
- 1966 – The first orbiting astronomical observatory is launched by NASA sourcing energy from a 1000 kW array. Named OSO – 1, it would make a continuous 1,038 orbits before the onboard recording tape would fail and would only transmit when it passed over relay stations.
Road to 21st Century
As the population soared after the two world wars, increased demand for energy came about. The space race also gave rise to the necessity of implementing solar technology with spacecraft. Paired with the revelation of global warming, the decades leading up to the 21st century saw a revamped interest in solar-derived energy. Advancements continue being made throughout this stage in the history of solar energy.
- 1970’s – U.S Energy crisis causes the necessity for alternative energy sources. Petroleum supply ran low and therefore prices skyrocketed.
- 1973 – University of Delaware creates the first building powered and heated solely by the solar panels attached to the roof. Named “Solar One”, the house proved that powering domestic residences was possible through the energy generated from solar panels.
- 1974 – As a result of the U.S energy crisis, congress passed the “Solar Energy Research, Development, and Demonstration Act of 1974. It was intended to boost the interest in progressing the development of solar technologies.
- 1979 – U.S President Jimmy Carter installs solar panels on the roof of the White House.
- 1980s – The United States experiences a significant drop in fossil fuel costs and a booming economy caused the public to lose interest in alternative energy sources.
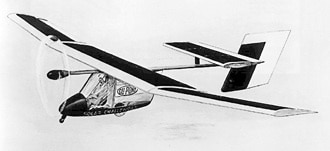
- 1981 – Paul MacCready builds the “Solar Challenger”, the first aircraft to be powered by solar energy. The pane carried over 16,000 solar cells producing 3,800 watts.
- 1985 – University of South Wales increases solar efficiency from 14% to 20%. They would go on to make the latest improvement in 2014 raising efficiency to 40%
- 1999 – The National Renewable Energy Lab teamed up with Spectro Lab and rose solar efficiency to 33.3%
- 2006 – United States enacts “Solar Investment Tax Credit” in order to incentivize the public to switch to solar energy.
Today, solar energy accounts for over 3% of all energy consumption in the United States and that number continues to grow each year. Since 2014, the cost of solar panels has dropped nearly 70%. With a continued decline in the cost of production and the increasing availability of solar panels, converting to solar energy has never been more beneficial and easy to access. The history of solar panels is rich but the future of solar technologies is bright like the sun
If you would like to experience the difference that solar can make on your energy bill and on the climate, contact Lumina Solar and allow one of our Solar Representatives to assist you in deciding which solar plan is best for you. Contact us today to get started!